Inventory Variance
The EBMS Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) section contains the total purchases for the given period. The inventory variance reflects the inventory value change. This value adjusts the purchase totals to calculate the cost of goods sold. The following set of accounts should be grouped together within the Cost of Goods Sold folder in the EBMS Chart of Accounts:
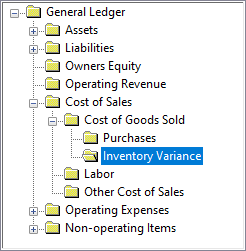
Cost of Goods Sold = Purchases + Inventory Variance
The inventory variance account is affected each time track count inventory is purchased or sold. The G/L account for Inventory Variance is set within the Advanced tab of each product record, along with the purchase, sales, and inventory asset accounts. Review the Advanced tab section of the Changing Inventory Defaults section for more details.
Variance is the difference between the Cost of Goods Sold and Purchases. (Cost of Goods Sold - Purchases = Inventory Variance). Note that the inventory variance value is negative when the inventory value is increased. A positive inventory variance indicates a reduction in inventory since the cost of goods sold value is greater than the amount of product purchased (Purchases account balance) for the given period.
Example 1
-
Purchases: $1,000
-
Sales: $700
-
Cost of Goods Sold: $400
Variance = $-600 (400 COGS - 1000 Purchases)
Cost of Goods Sold = $400 (1000 Purchases + -600 Variance)
Profit & Loss (P&L) will show:
-
Sales: $700.00
-
Cost of Goods Sold:
-
Purchases: $1,000
-
Variance: $-600
-
Cost of Goods Sold: $400
-
Gross Profit: $300
Example 2
-
Purchases: $400
-
Sales: $1,300
-
Cost of Goods Sold: $1,000
Variance = $600 ($1,000 COGS - 400 Purchases)
Cost of Goods Sold = $1,000 (400 Purchases + 600 Variance)
Profit & Loss (P&L) will show:
-
Sales: $1,300
-
Cost of Goods Sold:
-
Purchases: $400
-
Variance: $600
-
Cost of Goods Sold: $1,000
-
Gross Profit: $300
Example 3
-
Purchases: $1,000
-
Sales: $2,500
-
Cost of Sales: $1,800
Variance = $800 (1,800 COGS - 1,000 Purchase)
Cost of Goods Sold = $1,800 (1,000 Purchases + 800 Variance)
Profit & Loss (P&L) will show:
-
Sales: $2,500
-
Cost of Goods Sold:
-
Purchases: $1,000
-
Variance: $800
-
Cost of Goods Sold: $1,800
-
Gross Profit: $700
Use Single Cost of Goods Account
EBMS contains an option to disable the variance account by enabling the Use single G/L account option found in Inventory > Options > General tab > Cost of Goods section as shown below.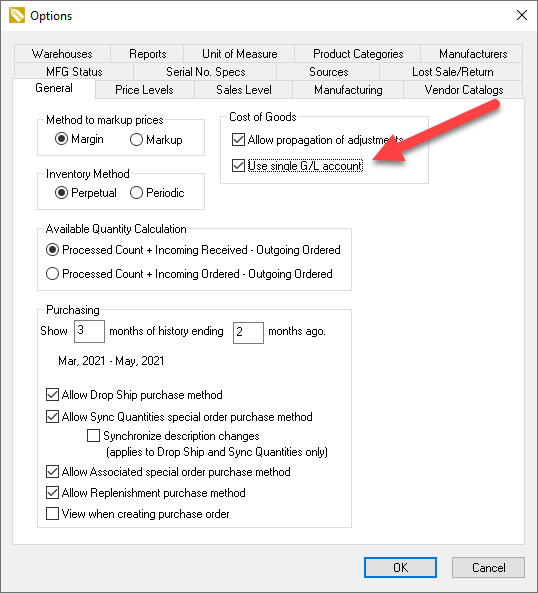
Variance Reports
Variance reports the following:
-
Inventory Asset:
-
If the variance is negative, it tells the user that not everything that was purchased within this period was sold, so the inventory asset increased by this amount of the negative variance.
-
If the variance is positive, it tells the user that everything that was purchased (as well as everything purchased in previous period) was sold, so the inventory asset decreased by the amount of the positive variance.
-
-
Variance allows the user to see purchases and then shows the difference between the beginning and ending inventory value.
-
Most ERP systems, including QuickBooks, only show one account (Cost of Goods Sold). So they will not show the purchases, because the total purchase value is not shown in the COGS section but is recorded in the inventory asset account.
-
Accounts Being Affected when Processing an Expense or Sales Document
Accounts Payable (A/P) Expense Invoice Process:
-
Purchases increased
-
Inventory Variance decreased*
-
Inventory Asset increased*
-
Accounts Payable increased
Accounts Receivable (A/R) Sales Invoice Process:
-
Revenue increased
-
Inventory Variance increased*
-
Inventory Asset decreased*
-
Accounts Receivable increased
EBMS creates the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) transaction by debiting the inventory variance account when an item is sold. The COGS balance is unchanged when a track count item is purchased. The purchase account is increased when inventory is purchased but is immediately offset by the credit value within the inventory variance account.
Important note: No Count Items within EBMS do not create the inventory variance and inventory asset transactions. Review the Inventory Classifications section for more details on the Track Count, No Count, and other inventory classification options.
In EBMS, No Count items are being expensed at the time of purchase. Therefore, the following should be considered:
-
A different purchase account may need to be used for No Count items (default response if to not separate this)
Important: If you are using EBMS departments, it is important that the correct department is specified in the Purchase account since the item should not be expensed to the 000 account but to the correct department.
Inventory Variance Transactions with Departments
All Inventory Variance G/L settings within EBMS only contain the 5-digit portion of the general ledger account. The 3-digit codes are always derived from the 3-digit extension of the purchase or sales G/L code to complete the 5-3 digit General Ledger account of the variance transactions. (The format will look like this: 00000-000) This process will maintain the integrity of the cost of sales transaction. For example, the following transactions are created if an $8 dirt shovel is sold for $12:
- Purchase: The cost of sales transaction for department 010 is unaffected, since the variance transaction cancels the purchase transaction.
9-digit purchase G/L code is debited (A): $8.00 purchase.
5-digit variance code (circled) + 3-digit department ( -010 from purchase code) is credited: $8.00 variance.
------------------
The result is not affected on the cost of sales total for department 010: $0.00
- Sales: The cost of sales transaction for department 010 is calculated using the sales and variance transactions, as shown below:
9-digit Sales G/L code is credited (B): $12.00 sales
5-digit variance code (circled) + 3-digit department ( -010 from sales code) is debited: $ 8.00 COS
------------------
The result is a profit for department 010: $ 4.00 profit
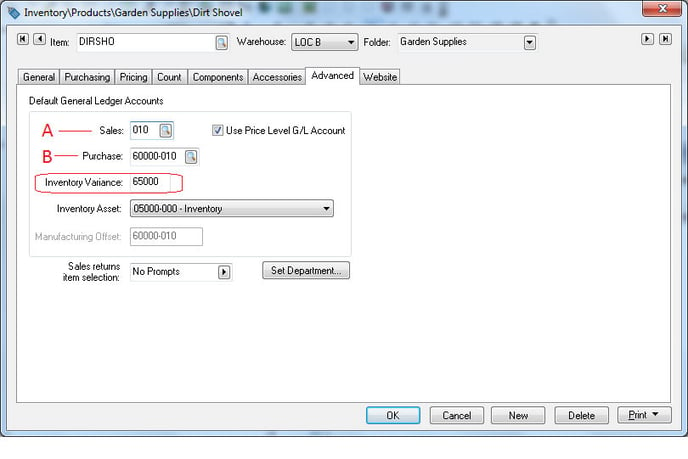
Sold from a different department: An item may be sold using a different 3-digit department extension than the original purchase. This difference may happen in the following situations:
-
-
The sales General Ledger code is changed by the user within the sales invoice.
-
The department setting controls the department code of a sales G/L code. Review the Using a Department as a Company Division or Location for more details.
-
The product is transferred from one warehouse to another. The warehouse setting may affect the sales G/L code. Review the Multiple Location section for details on selling product from multiple locations.
-
The cost of sales transaction for department 020 is calculated using the sales and variance transactions as shown below:
9-digit Sales G/L code with an extension of 020 is credited: $12.00 sales.
5-digit variance code (circled) + 3-digit department (-020 from 2nd department) is debited: $ 8.00 COS.
------------------
The result is a profit for department 020: $4.00 profit.
The cost of sales cost for department 010 remains at zero. (See steps above.)
The inventory variance account is only used when the inventory method is set to Perpetual. Go to Inventory > Options > General tab to view the inventory methods setting.