All worker taxes, worker deductions, and company taxes must be set up within the Labor > Taxes/Deduction window before they can be used within payroll. EBMS allows a variety of rate calculations to accommodate the large number of different payroll taxes and deductions. It is very important that these tax and deduction rates are properly set up before any payroll is processed. Contact an accountant or a Koble Systems consultant if you need assistance in configuring your taxes or wish to add a complex deduction. EBMS comes with multiple taxes already set up that can be added to or edited. Go to Changing Tax/Deduction Rates for details.
To add new taxes or deductions take the following steps:
-
Go to and the following window will appear.

-
Click on New button and the following wizard will start.

-
On the Description page, select the Tax Type or deduction type by choosing an option from the dropdown list. The dropdown list can be opened by clicking on the down arrow to the right of the Tax Type field. It is important to select the proper type because:
-
The wizard will ask appropriate questions based on this type.
-
Payroll register reports sort taxes and deductions in the order determined by this type.
-
This type determines the location within tax forms such as W2s.
-
Manual adjustments will be or not be allowed depending on the type.
-
Prevailing wage rates are calculated based on variables connected to this type.
-
If none of the types apply to the tax or deduction that you are entering, choose Other – other deduction as the Tax Type. Consult with your accountant or a Koble Systems consultant before creating a new tax if you are unsure of which type to choose.
-
-
Enter a detailed Description explaining the tax or deductions. The description will default to the tax type description, but it can be easily changed.
-
Set the Payment Frequency based on the scheduled payment of the tax to the tax agency
-
Select the Tax/Deduction option. (Review the Tax Links article for details on the tax link option.) Click the Next button and the following window will appear:

-
On the Details page, select the appropriate How is this tax calculated? option. The options available are:
-
Tax Table option is used for taxes such as Federal Withholding Tax and some state taxes that used graduated tax rates.
-
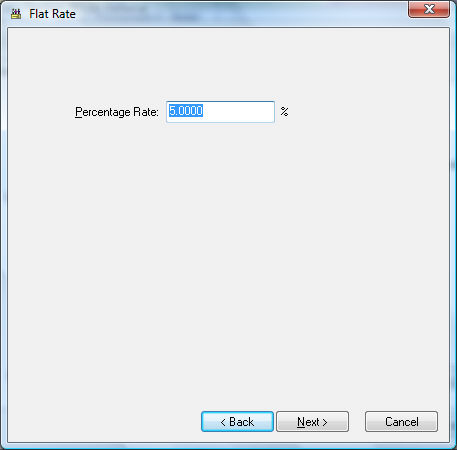
Flat Percent Rate option is used for taxes that calculate the deduction based on a certain percentage of gross wages. Withholding Taxes such as Social Security tax, unemployment taxes, and many state and local taxes use this method as well as many common worker deductions.
-
Flat Dollar Amount option should be used when a set dollar amount is required to be deducted, such as OPT withholding tax.
-
If Manual Tax is selected, the user will be prompted to enter the tax or deduction amount each time the timecard is processed. This option is convenient when the deduction is not standard.
-
The Benefit Adjustment option is used when a benefit is given to a worker and the Worker is obligated to pay tax on the value of the benefit. This adjustment is not withheld from or added to the paycheck but is added to the gross pay when other taxes are calculated. This adjustment is sometimes called a gross-up. See Benefit Pay section for more details.
-
-
Enter the Liability G/L account that you wish to accrue this tax or deduction. All taxes and deductions should be accrued in a General Ledger liability account and be reconciled on a regular basis to assure that the total withheld equals the total paid to the tax or benefit vendor. The G/L account must have a classification of Payroll Tax/Deduction to be listed as an available account. Click Next to continue.
-
The next wizard page depends on How the tax is calculated setting. Move to the appropriate section, skipping the settings that do not apply. The following rate and pretax pages (the next 2 pages) only apply if the deduction rate is set to Tax Table or Flat Rate as shown below:
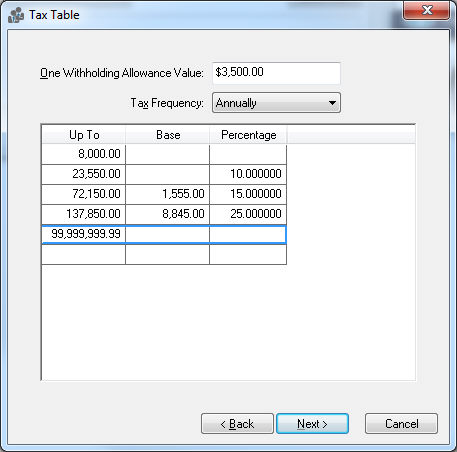
Tax Table
-
Withholding Allowance: Enter the exemption allowance for the new tax or deduction. This is important for taxes such as Federal Withholding Tax as well as any other tax that gives a deduction based on the number of exemptions. Keep this field blank if there is no withholding allowance.
-
The Tax Frequency identifies the tax period that the table is based upon. For example, if the Tax Frequency is annual and timecards are processed weekly, the rates would be divisible by 52. If the Tax Frequency equals weekly and timecards are processed bi-weekly, the rates are multiplied by two.
-
The Up To, Base, and Percentage columns are used to enter a graduated tax table. The Up To identifies the range, The Base the base dollar amount, and the Percentage the additional percentage amount.
Flat Percent Rate
-
Flat Dollar Amount dialog is similar to the Flat Percent Rate dialog.
-
Manual and Benefit Adjustment deductions ignore the rate page since rates are entered manually on the timecard.
-
-
Click the Next button and the following Minimums / Maximums window will appear:
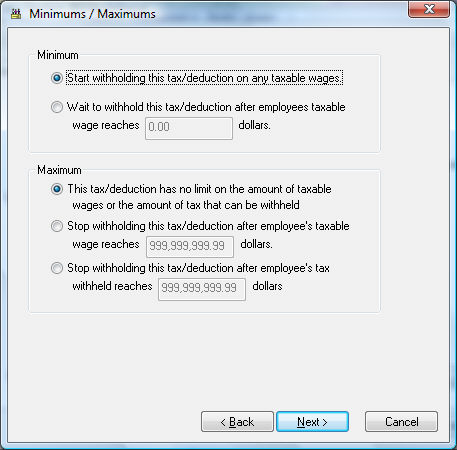
-
Set the appropriate Minimums and Maximums for the tax. Select the first options within the Minimum and Maximum option boxes if the tax or deductions should be deducted on all pay.
For Minimum, the first option will be "Start withholding this tax/deduction on any taxable wages."
For Maximum, the first option will be "This tax/deduction has no limit on the amount of taxable wages or the amount of tax that can be withheld."
-
If the pay is not to be deducted on the first part of the pay, select the second option and enter the gross pay amount that must be earned before tax is deducted.
For Minimum, the second option will be "Wait to withhold this tax/deduction after employees taxable wage reaches [ ] dollars."
For Maximum, the second option will be "Stop withholding this tax/deduction after employee's taxable wage reaches [ ] dollars." -
If there are limits to the amount that is to be deducted from the Worker’s pay, then set the appropriate option. Set to the second option if the limit is wage-based or set the third option if limit is tax-based. (The third option for Maximum is "Stop withholding this tax/deduction after employee's tax withheld reaches [ ] dollars.")
-
-
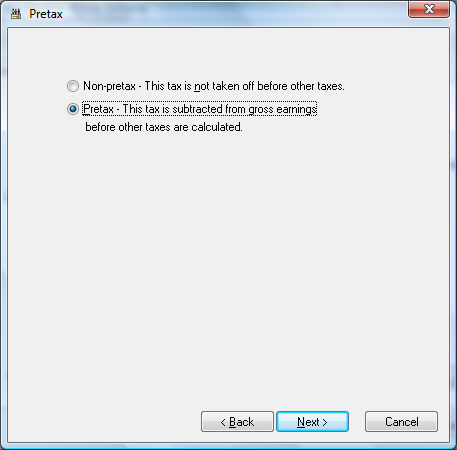
Click the Next button and the following Pretax window will appear:
-
Set the first option if the tax or deduction is not pretax. This option is listed as "Non-pretax - This tax is not taken off before other taxes."
-
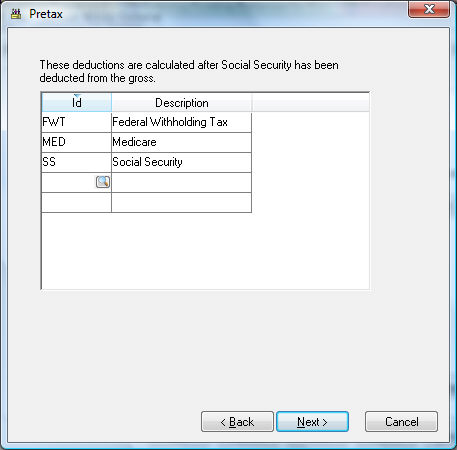
Set the second option if the tax is pretax. This option is listed as "Pretax - This tax is subtracted from gross earnings before other taxes are calculated." The second option is set (Pretax), the deduction will be deducted from the gross wages before other (non-pretax) taxes and deductions are processed. This option is commonly used for medical benefits, which does not require the worker to pay taxes on the benefits that are deducted from his or her pay. If the Pretax option is enabled, the following page will appear when Next is clicked.
-
You must list all taxes that are calculated after the pretax deduction is calculated. For example, if a health benefit deduction can be pretax for Social Security, Medicare, and Federal Withholding taxes, then list FWT, FICA, and MED tax codes in the pretax list. To add taxes to the pretax list, click on a blank line in the list, click on the magnifying glass lookup icon, and select the appropriate taxes. Click Next when list is complete.
-
-
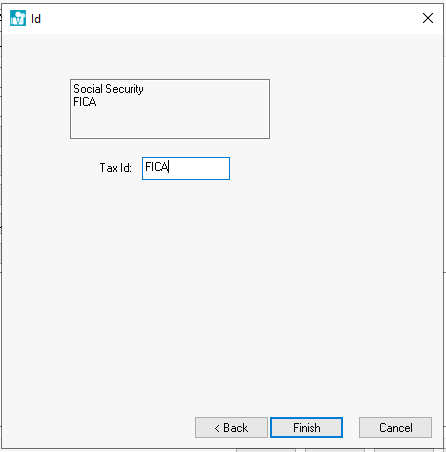
On the ID page, enter the Deduction or Tax Id. This code is required to be unique for a specific tax or deduction. This Tax ID is used throughout the entire accounting system for all transactions associated with this tax or deduction. The Tax ID for a state withholding tax should be labeled with the state’s 2-character abbreviation. For example, add NJ to label the ID for New Jersey withholding tax. Review Process and Print W2s for specific reasons for this requirement.
-
Click Finish to create the new tax or deduction or Cancel to leave without saving any changes.
Review Calculating Taxes for instructions on processing taxes and deductions within payroll.
