Multiple Codebase Services
When to use multiple Codebase instances and how to add a new Codebase ODBC server
Codebase Service is the back-end database engine used by EBMS. The default deployment of the EBMS server components creates a single instance of Codebase on the server machine. This means that all connections to the database (desktop users, mobile users, background services) go through that single instance. That single Codebase instance is then both a potential point of failure and performance bottleneck for overall EBMS availability and scalability.
The administrator may configure additional Codebase instances to improve availability and scalability, after which he can assign users and background services as he wishes among the pool of instances.
Some example configurations (not mutually exclusive):
- MyEBMS (REST API and Mobile) on a separate Codebase instance from desktop users.
- Each company is assigned to a separate Codebase instance.
- Each department is assigned to a separate Codebase instance.
- Power users are assigned to their own Codebase instance.
- Remote XPressPOS and web synchronization are assigned to their own Codebase instances.
Why Use Multiple Services?
A single Codebase server creates the following problem of multiple users and servers hitting the codebase service simultaneously.
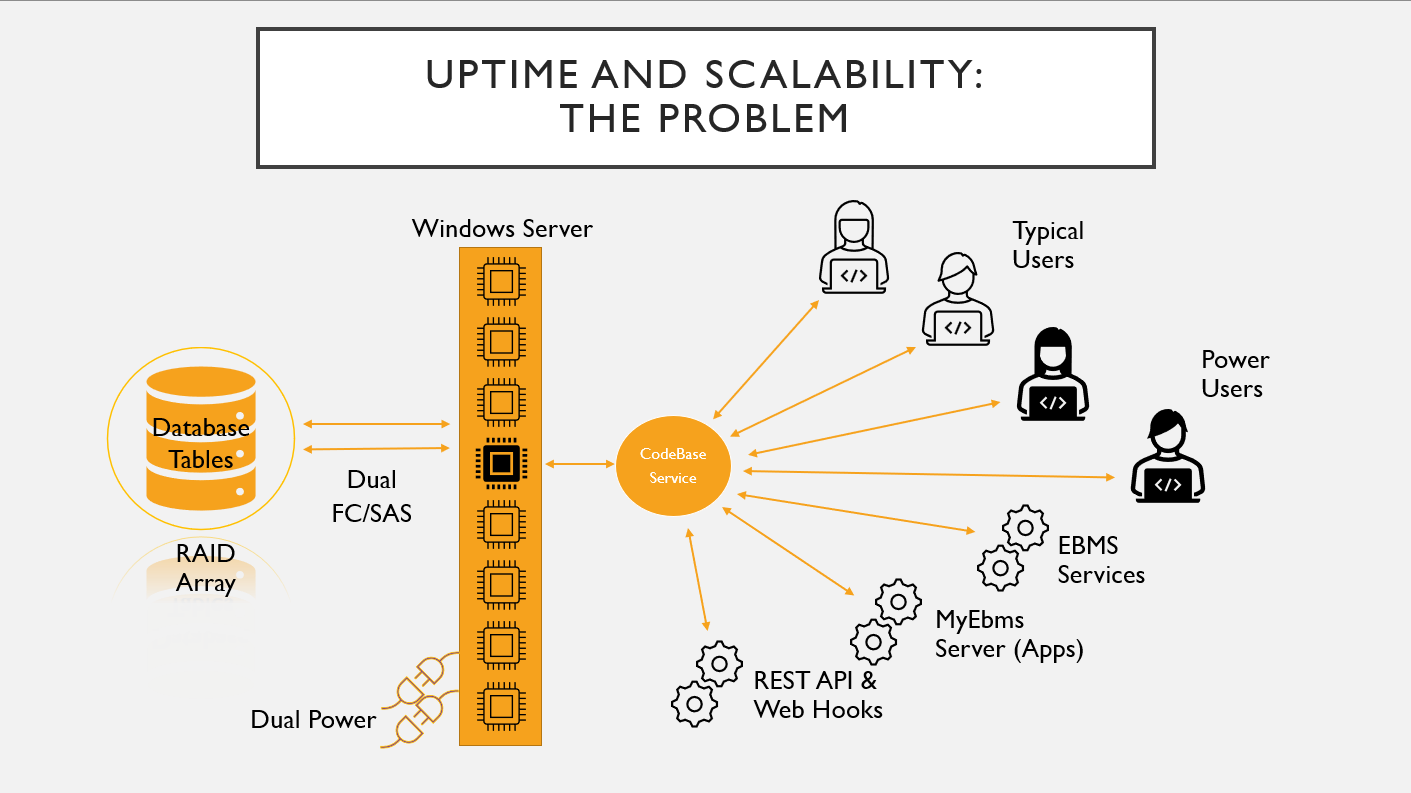
Two or more Codebase services may be the solution to enhance performance or increase uptime. The fail-over switching of redundant services is useful to reduce down-time. Multiple Codebase services should keep EBMS from crashing.
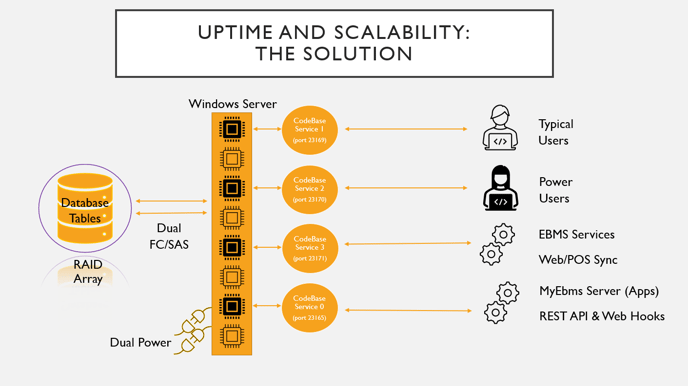 Multiple Codebase services should be only used if there is heavy database traffic. If the Codebase traffic is light, multiple instances will result in very little performance improvement. If the Codebase traffic is heavy and the single instance causes a performance bottleneck, multiple instances can result in major performance improvements.
Multiple Codebase services should be only used if there is heavy database traffic. If the Codebase traffic is light, multiple instances will result in very little performance improvement. If the Codebase traffic is heavy and the single instance causes a performance bottleneck, multiple instances can result in major performance improvements.
Creating Multiple Services
Multiple services should be configured by the network administrator or IT staff. Complete the following steps to configure additional Codebase services.
-
Launch EBMS Server Manager. Review Server Manager Overview for more details on this tool.
-
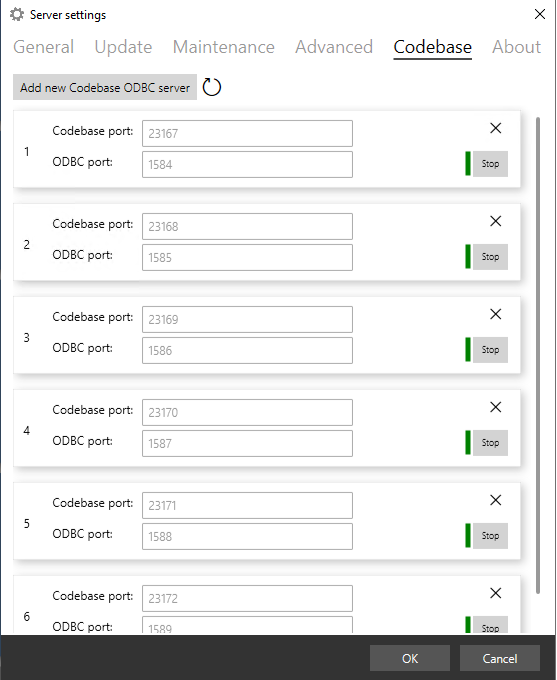
Open the Settings page and click on the Codebase tab.
-
Click Add new Codebase ODBC server and enter a Codebase port number and ODBC port value as obtained from your network administrator.
-
Repeat for additional services.
EBMS does not enforce the administrator's assignment of users to Codebase instances. This allows a user to change to a different instance if needed and without having to contact the EBMS administrator.
Review Login Procedures to assign users to each Codebase service.