Accounting financial transactions are created each time an invoice is processed, payment is made, or any other financial document is processed within EBMS. All the transaction records created from various EBMS modules are posted to the financial system to update the financial totals in the system.
Video: Adjusting Financial Accounts ERP Support Training
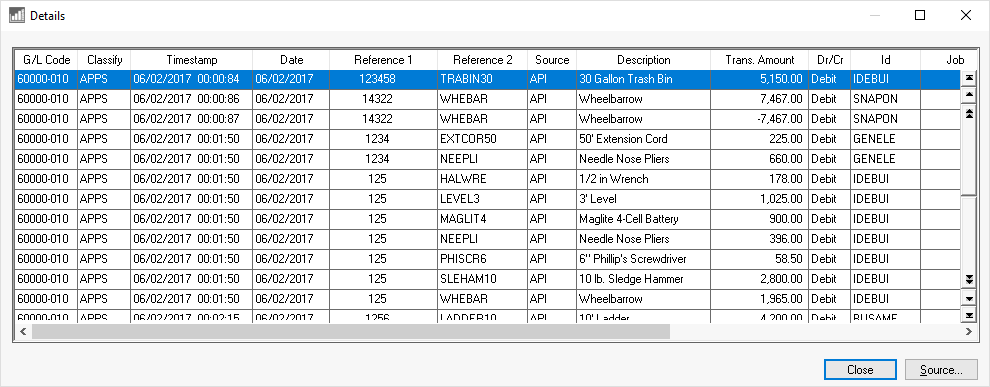
These individual transactions contain valuable information including, but not limited to, the following:
-
General Ledger account: This code identifies the posted G/L account.
-
Financial classification: The classification codes that indicates how EBMS will handle a transaction.
-
User login name, date, time of each transaction: This is useful to determine who performed the transaction and a date stamp for when each transaction happened.
-
Transaction Date: Identifies the fiscal post date of the transaction.
-
Reference: These codes will give further information such as invoice number and other codes to reference the source documents.
-
Source: A code identifies which document within EBMS created the transaction. For example, the code ARI indicates that an Accounts Receivable invoice created the invoice.
-
Description: Visual description that was entered within the notes or descriptions of the document.
-
Debit or Credit indicator.
-
ID: Includes an account ID (such as a customer, worker, vendor, or other code).
-
Job Codes: Review the Changing Job Information for more details on job settings.
-
Technical codes such as the Post Stamp or Record Type that power the comprehensive audit trail of EBMS: Review the Find the Source Documents Using the Financial Audit Trail section for more audit trail details.
-
And additional other details that allow the software to post the accounting transaction to the proper accounts as well as identify the source details of the transaction.
Note that the financial transactions are never changed or deleted after they are posted. Reverse transactions are created when a document or voided, unprocessed, or deleted. Transaction records
Creating Transactions
Processing invoices, purchases, payments, taxes, timecards, journals, and other dialogs within EBMS create general ledger transactions when documents are processed (as diagramed below):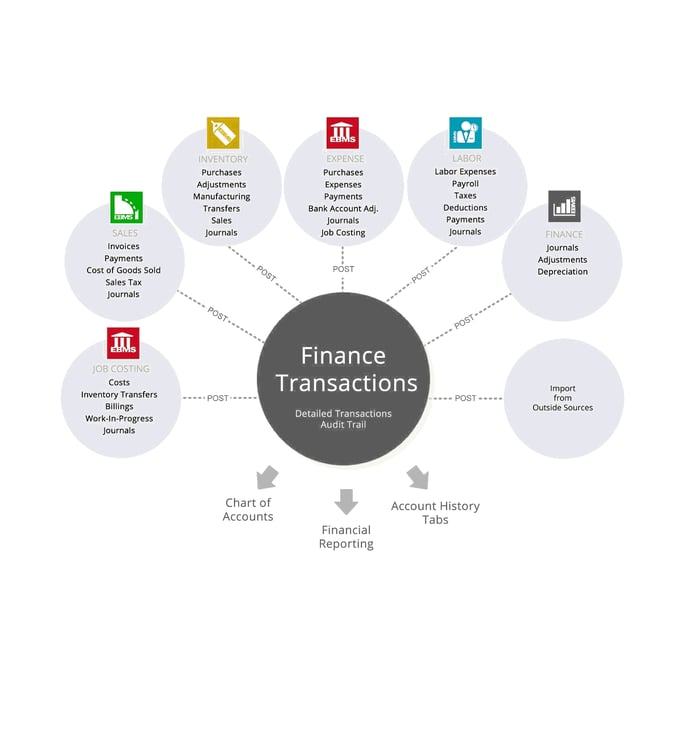
The multiple light gray circles are a diagram of the unposted transactions created from multiple modules within EBMS. The transaction sources are listed within each circle. Continue with the following sections to review the tools that post unposted transactions from the original temporary location (light gray) to the permanent location (dark gray) and also updates the chart of accounts, account history tabs, and the financial reports.
Viewing Unposted Transactions
Transactions are placed into an unposted transaction file at the time a document, payment, or journal is processed.
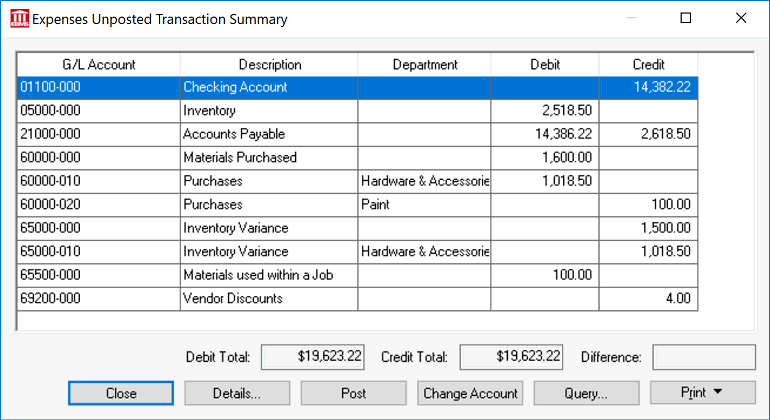
The Display Unposted Transactions dialog can be used to view financial transactions or correct any transaction issues such as an incorrect date, a date within a closed period, an invalid general ledger account, or imbalance totals.
Steps to correct a financial transaction:
-
Go to or find Display Unposted Transactions under any header (Sales, Inventory, Expenses, Labor) from the EBMS main menu to open an unposted transactions dialog:
-
To display a detailed list of transactions, click the Details button. Highlight the transaction that is creating the problem and click Source to identify the source of the transaction.
-
Click the Change Account button to change the general ledger account. This is the best way to correct a bad general ledger account problem as shown in the example above.
-
Click the Query button to list a subgroup of transactions based on specific criteria. Review Query Options for details on querying information.
-
When the problem is fixed, click the Post button and post the transactions. When the transactions have posted, you will be returned to the main window.
-
The Financials > Display Unposted Transactions > By Date dialog will be in the same type of window but only lists the transaction date and debit and credit amounts as opposed to the By G/L Account dialog, which also lists the GL account, description, and department if applicable.
Note that unposted transactions can be viewed within the Sales, Inventory, Expenses, Labor, as well as the Financials menu. Where you access unposted transactions changes which transactions you see (for example, Sales > Display Unposted Transactions will show you all unposted sales transactions, but no inventory transactions). There is an option to Post All Transactions in the Financials menu and that will post all unposted transactions, regardless of the section.
Posting Transactions
Select the Post button to update general ledger totals and history tab totals. The post transaction step includes a number of steps to guarantee accurate posting.
-
After clicking post in a module-specific Display Unposted Transactions dialog or clicking Post All Transactions under the Financials menu, transactions are copied from the unposted transaction file to the financial transaction detail file. The financial transaction within the detail file can be viewed by drilling down (right clicking) on any general ledger total or history tab amount.
-
Other places to find financial summaries:
-
The general ledger account totals within the Chart of Accounts: Many of the financial statements such as the balance sheet, profit & loss, or trial balance are derived from the GL chart of account totals. Review the Adding General Ledger Accounts section for more details on the chart of account setup.
-
G/L account history tabs: The history totals can be viewed on the year tabs of a customer, vendor, inventory items, employee, etc. Review the Account History Tabs section to review the summary pages for these transactions and to view the financial transactions that link the totals to the source documents.
-
Department summary tabs: The summary totals per department are listed within the department accounts. A department can be a location, profit center, or individual departments. Review the Department and Profit Center Overview section.
-
Note: Bank account and cash account balances are not affected until transactions are posted.
Go to to post all un-posted transactions within all the modules of EBMS. This step combines all the post processes within the individual modules.
The financial transactions within EBMS are used as the foundation to the powerful audit trail tools of EBMS. Review the Find the Source Documents Using the Transaction Audit Trail section for more details.
Transaction Reporting
The general ledger transaction detail file is the complete source of accounting details. Not only does it contain the individual debit and credit values, but it also contains document source details and the user, date, and timestamp information that identifies who created the transaction and when the transaction was created. EBMS contains reporting options to view these transaction details. Select from the main EBMS menu and select the File > Reports > Financials > Transactions group as shown below: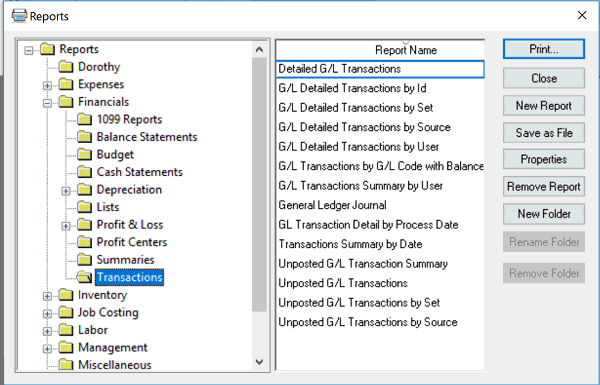
Select the following reports to display transaction detail:
-
Use the Detailed G/L Transactions report to view a list of transactions by General Ledger account codes or date range.
-
Use the G/L Detailed Transactions by ID to group or summarize transactions by the ID. This report can be used to summarize transactions within a GL code by the customer, vendor, worker, or other ID.
-
Use the G/L Detailed Transactions by Source to group transactions by the source code such as a sales invoice (ARI), expense invoice (API), timecard (PYT), etc.
-
Use the G/L Detailed Transactions by User report by group transactions by the login user.
