Budget Overview
Set a budget, meet goals, and evaluate your company's financial condition.
In this article
Getting Started | Features | Sample Reports and Scenarios
Getting Started
Budgeting is an important and necessary part of small business management. Many lenders and investors require a budget before they agree to partner with a company. More importantly, a budget can be a valuable tool to help the business owner meet goals and stay abreast of the financial condition of a business.
A budget is really just a financial plan. It can be as simple or as complex as needed, although a certain level of detail is necessary to make it effective. With that in mind, here are some tips to help you get started.
This optional EBMS module is not included on all versions of the EBMS software. Review the Optional EBMS modules for specific instructions used to identify or add optional modules.
The EBMS Budget module is an important management tool using to generate the following information:
- Project revenue projections for the current year as well as future fiscal years
- Budget cost of sales targets based on gross margin projections
- Budget labor and other direct costs for a department or process based on percent of sale or other ratios
- Budget overhead costs based on a fixed amount or ratio
EBMS budget calculations allow the user to create a budget for the new year or project revenue or budget expenses for future years even if the EBMS fiscal year is not opened.
Budgets can be created for a specific department or profit center to give specific managers goals and budgets. Review Allocating Indirect Expenses to a Profit Center section for details on setting ratios that also effect budgets.
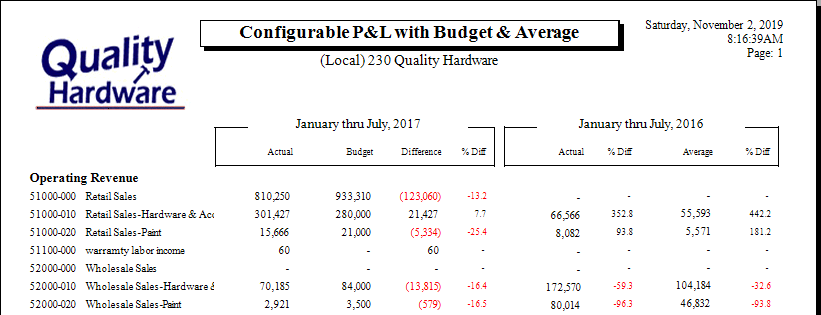
The EBMS software contains many reports to compare actual income and expenses with the budget. The budget system can be used to project profits and create side-by-side comparisons to measure the progress of the company. Review the budget reports by selecting File > Reports > Financials > Profit and Loss reports from the main EBMS menu.
The budget values for a specific year can be found by selecting Financials > Budget from the main EBMS menu to open the following budget dialog: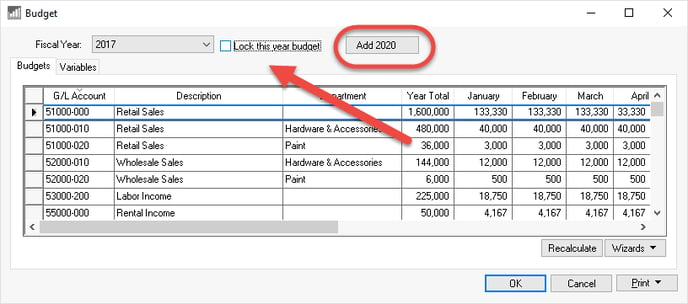
Select the Fiscal Year to view or change values for a specific year.
Click on the Add Year button to create a new budget year (see circled button in image shown above). Budget projections can be created for future periods before the fiscal year is open.
Enable the Lock this year budget to keep the budget amounts from being recalculated or to keep users from altering the budget amounts.
The budget module within the EBMS system contains tools to set budget values in a variety of methods:
-
Manually created budget by month or year: Review the Creating a Simple Budget section for details.
-
Formulas based on percent of sales or ratio of another expense: Review the Calculating a Budget Using a Formula section for details.
-
Projections or budgets based on previous years.
-
Set formulas for a range of accounts. Review the Change a Range of Budget Accounts section for details.
-
Ability to create formulas and variables to calculate a budget value based on a combination of factors. Review the Using Variables section for details.
-
Import information from an Excel spreadsheet. Review the Connecting the Budget to a Spreadsheet section for details.
-
Set budgets based on monthly values rather than annual totals. Review the Monthly Budgets section for details.
Start with a simple budget and add complexity by using formulas and variables as needed. Continue with the following steps for details on the budget module of EBMS.
Common use cases
Project Income and Profits
The EBMS Budget module is an important management tool used to project a plan for the New Year or additional future years. This projection becomes a guide to compare actual expenses and income to the projection or budget. The budget system can be used to project income and profits and create a comparison picture to measure the progress of the company.
Set Monthly & Annual Budgets
Set monthly and annual budgets, calculate your budget with formulas based on percentages of actual sales and expenses, and more. This allows the business manager to get an accurate picture of how the company is progressing toward set goals.
The EBMS Budget module can help answer the following question you may have about your business:
- Will I have the income to pay for projected expenses?
- Are my current sales and expenses meeting the goals required to earn my projected profits?
- Are my overhead costs within a manageable level?
- Do I have the information needed to decide the company's financial decisions.
Start with a simple budget and add complexity by using formulas and variables as needed.
Features
- Create a budget by month or year
- Automatically adjust the budget for a specific account based on percentages based on a previous year's budget, projected sales, payroll, cost of sales, etc.
- Budget based on previous years
- Set budget formulas for a range of General Ledger accounts
- Create formulas and variables to calculate a budget based on a combination of factors
- Import information from an Excel spreadsheet
- Set budgets based on monthly values rather than annual totals
- Do basic calculations from variables, account budget, or past year values with included formulas
- Calculate monthly budget by distributing the annual budget evenly, same as last year or based on a user-entered monthly percentage
- Start with a simple budget and add complexity by using formulas and variables as needed
Sample Reports
Scenarios
Scenario 1: A building supply center is required to create projections for the bank. Management sets individual projected revenue targets for the lumber, building supplies, and door and window departments as well as projected sales for the hardware and tool store. The projected increase for the next three years may vary considerably between departments based on business goals, advertising, and demand. Management sets the projected lumber sales based on a fixed dollar amount since the market is very volatile. The team calculates the projected increase in hardware store sales and other departments based on a percentage increase for each year. The budgeted cost of sales costs is set based on a projected margin. Most overhead costs are calculated as a percent of sales for each year.
Scenario 2: An agricultural equipment sales and service company calculates projected sales based on a percent increase from previous years. The projected service revenue is calculated based on the estimated number of employee hours multiplied by the going service rate. The Cost of Goods Sold labor budget is based on the estimated number of employees multiplied by the projected gross payroll. Labor overhead is calculated as a ratio of the gross payroll costs. Other overhead costs such as supplies, insurance, maintenance, legal, depreciation, and facility costs are calculated based on various ratios. The advertising budget and sales labor are calculated based on percent of sales. The budget can be adjusted monthly based on the month of the year since business is seasonal.
Scenario 3: A custom metal fabricating business sets their income projections and cost budgets based on labor capacity. Management sets the projected payroll labor costs as well as the subcontractor costs to manufacture the products their customer's need. The projected revenue is calculated from the total cost of goods sold using a projected margin for each year. The manufacturing overhead budget including the facility, rentals, and equipment deprecation are set based on current contracts. The other overhead budget amounts are calculated from the labor budget or projected sales.